NOTE: This test is ONLY AVAILABLE TO AUSTRALIAN RESIDENTS.
How good is your Immunity? Take the Immune Cytokine test and discover the truth about your immunity.
About Cytokines
Cytokines serve as molecular messengers between cells mediating normal cellular processes in the body. Cytokines interact with cells of the immune system regulating various inflammatory responses to disease and infection. Cytokines are released by cells into the circulation or directly into tissue. The cytokines locate target immune cells and interact with receptors on the target immune cells by binding to them. The interaction triggers or stimulates specific responses by the target cells. The Cytokine Immune Test assesses both Pro-Inflammatory and Anti-inflammatory groups of cytokines and gives information on up/down regulation needs.
Cytokine imbalances are known to be involved in autoimmune disorders and immune dysfunction. Testing allows analysis of not only cytokine involvement in disease but it also provides an easy solution for monitoring therapy effectiveness.
About The Cytokine Test
After you purchase the Cytokine immune test, you will receive a simple blood test kit in the mail. The test kit comes with:
- An authorized blood specimen order form that you take to your local accredited pathology for collection of your blood (Find a pathology near you here).
- A blood specimen test kit for the pathology to use to collect your blood sample
- Complete instructions for taking the test for you and the pathology
Test results are sent to one of our professional health practitioners within 10 – 15 business days for evaluation. Our practitioners contact you with the results and recommendations on any findings via email, mail or phone.
What is tested exactly?
The Cytokine Immune test checks the following important immune markers:
- GM-CSF
- IFNγ
- IL-1B
- IL-2
- IL-4
- IL-5
- IL-6
- IL-7
- IL-8
- IL-10
- IL-12
- IL-13
- IL-17
- TNFα
- TNFB
- TGFB
Common Conditions associated with impaired Cytokines
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Hashimotos Thyroiditis
- Depression
- Recurrent miscarriages
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Asthma
- Eczema
- Food intolerances
- Poor immunity
- Inflammatory conditions
- Diseases associated with Cytokine activation e.g. flu, viruses etc
About Cytokines
Cytokines are signaling proteins and glycoproteins that mediate and regular immunity, inflammation and hematopoiesis. They are also involved in cell growth and differentiation, cell death, angiogenesis, normal development and neuromodulations.
Cytokines are critical to the functional both innate (cell-mediated) and adaptive (antigen specific/humoral) immune systems. They are known as either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory. Pro-inflammatory cytokines include interferon-gamma (INFγ), interleukin-2 (IL2) and interleukin-12 (IL12); whereas interleukin-4 (IL4) and interleukin-5 (IL5) are anti-inflammatory.
Generally pro-inflammatory cytokines are secreted from T-helper 1 (Th1) cells and anti-inflammatory cytokines are secreted from T-helper 2 (Th2) cells. Under normal circumstances the Th1 and Th2 systems should be in balance.
Cytokines and Disorders of the Immune System
Over-activation of either the Th1 or Th2 system can cause disease, being active even when there is no threat. When Th1 is dominating abnormally, organ specific autoimmune type diseases can result. On the other hand, when the Th2 system is dominating, disorders that are primarily allergy or antibody driven occur. The body becomes overly sensitive to ‘extracellular pathogens’, often reacting and producing antibodies against non‐pathogenic stimuli such as food and dust.
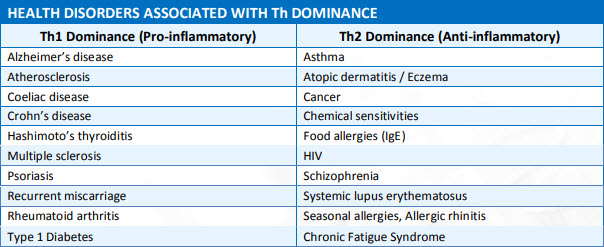
Blood cytokine levels are useful and important in the differential diagnosis of inflammatory disorders such as neutrophilia, eosinophilia, and in distinguishing tumour-caused fever from infectious fever in malignant lymphomas. Cytokines are critical to the functional both innate (cell-mediated) and adaptive (antigen specific/humoral) immune systems. They are known as either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory. Pro-inflammatory cytokines include interferon-gamma (INFγ), interleukin-2 (IL2) and interleukin-12 (IL12); whereas interleukin-4 (IL4) and interleukin-5 (IL5) are anti-inflammatory.






